
Brogen
- Email:inquiry@brogenmotors.com
- Whatsapp:+86 19352135902
- Wechat:Brogenmotors_SH
- Tel:+86 19352135902

Brogen
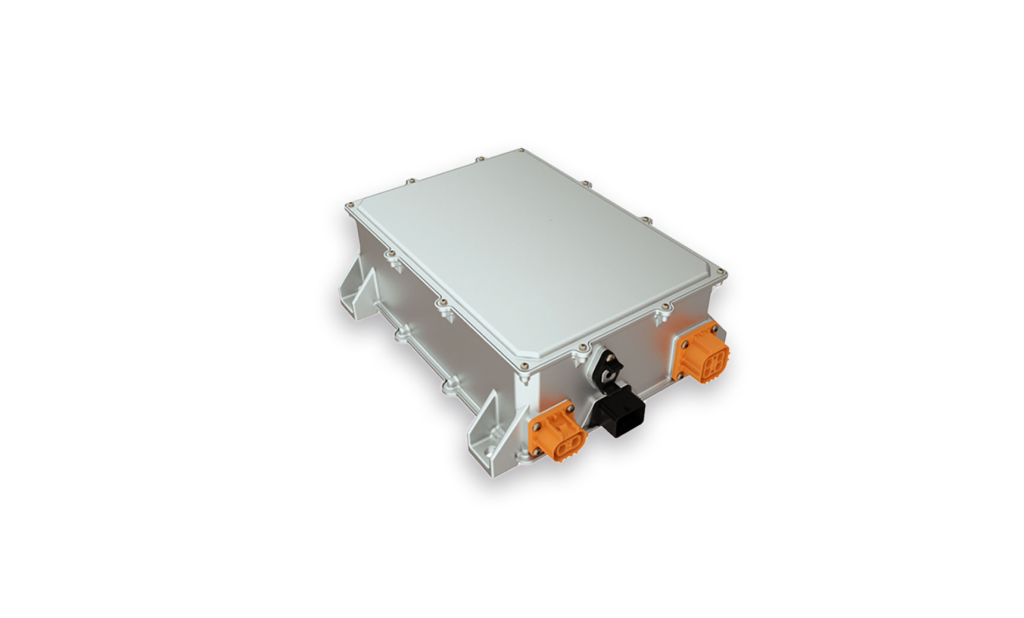

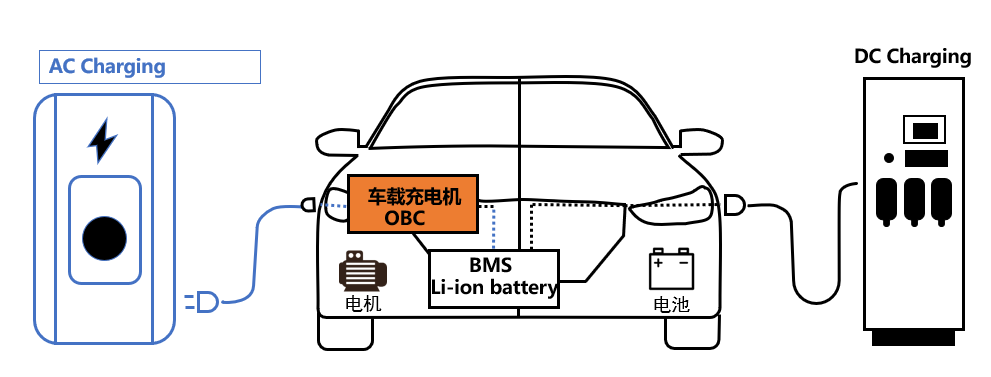
The on-board charger (OBC) in electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical component that transforms alternating current (AC) from charging stations into the direct current (DC) necessary for the vehicle's power battery. It is an essential piece of equipment for EVs that utilize AC charging infrastructure.

Image: Brogen 11kW OBC 2 in 1
The OBC serves as a multifaceted device in the EV ecosystem, with its primary function being the communication with the Battery Management System (BMS) and the vehicle's monitoring system. It engages with the BMS via the CAN high-speed network, dynamically adjusting the current and voltage output to match the optimal charging parameters as dictated by the BMS, thereby selecting the most efficient charging strategy for the battery pack.
During charging, the BMS vigilantly monitors the battery pack's voltage, current, temperature, and connection status to manage and safeguard the battery's health. It communicates with the vehicle's monitoring system over the CAN network, transmitting operational status, parameters, and any fault alerts, while also receiving commands to initiate or terminate the charging cycle.
The OBC is equipped with an array of safety features designed to protect the battery and prevent hazardous conditions such as overcharging, overheating, and short circuits. These include AC input overvoltage protection, undervoltage alarms, overcurrent safeguards, DC output overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, soft start capabilities, current surge prevention, and flame retardancy.
The OBC is composed of several key components: the AC input port, power unit, control unit, low-voltage auxiliary unit, and DC output port.
The AC input port facilitates the reception of AC power from the grid, typically featuring a 7-pin configuration with three connection types. It operates on a standard single-phase input of 220V at industrial frequency, with the option to engage two additional pin ports for a 380V input when higher power is necessary.
The power unit acts as the conduit for charging energy, encompassing an electromagnetic interference suppression module, a rectifier, a power factor correction module, a filter, a full-bridge conversion module, and a DC output module. In conjunction with the control unit, it converts the input AC power into DC voltage levels suitable for the power battery system.
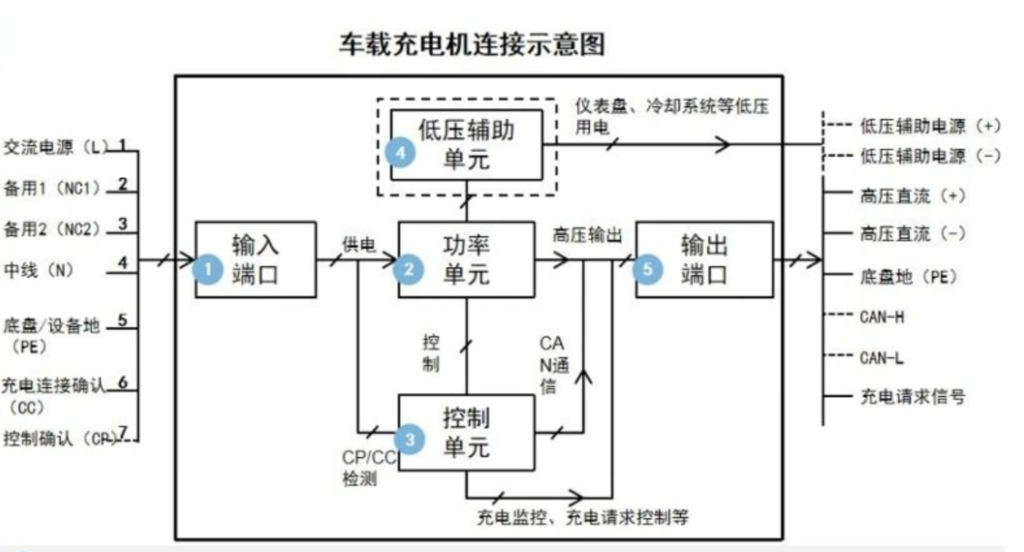
The control unit is the heart of the OBC, managing the power unit's conversion process through switching devices, executing precise closed-loop control for power conversion, and offering protective functions. It comprises primary detection and protection circuits, overcurrent detection and protection, overvoltage/undervoltage monitoring and protection, and a DSP main control module.
The low-voltage auxiliary unit supplies power to the control unit's electronic devices and facilitates system communication with external devices. It includes a CAN communication module, an auxiliary power module, and a human-computer interaction module.
The DC output port delivers DC power to the battery, featuring pin ports for the positive and negative terminals of the low-voltage auxiliary power supply, the positive and negative terminals of the high-voltage charging circuit, chassis ground, communication lines CANH and CANL (with the possibility of CAN shielding), and a charging request signal line.
For the latest news please view Brogen’s Linkedin. For more videos please click Brogen’s Youtube.
Connect with a Brogen expert to learn more about our services and discuss our ePowertrain solutions.
Company Profile